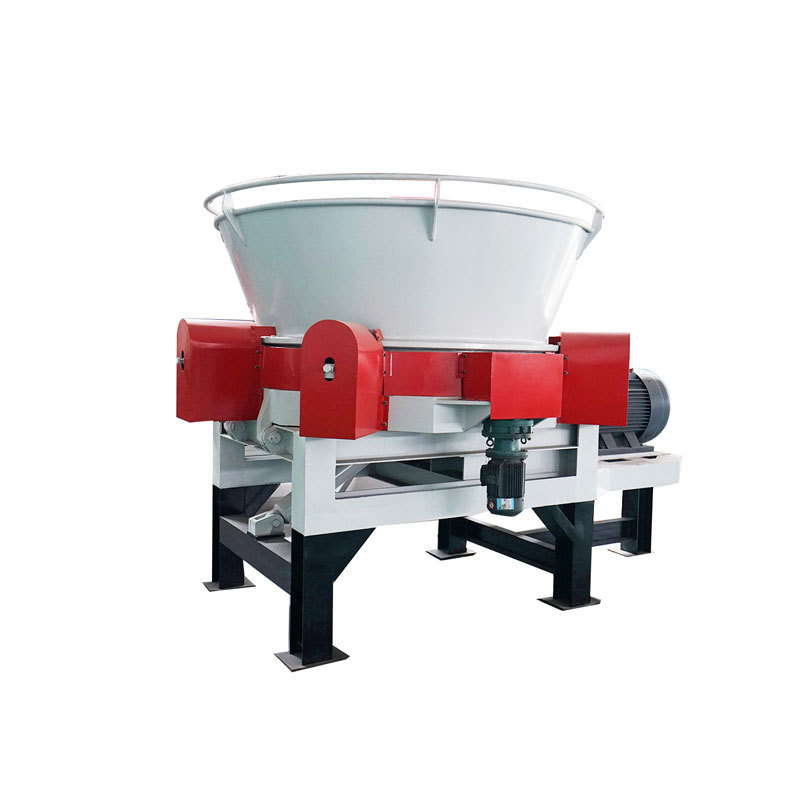
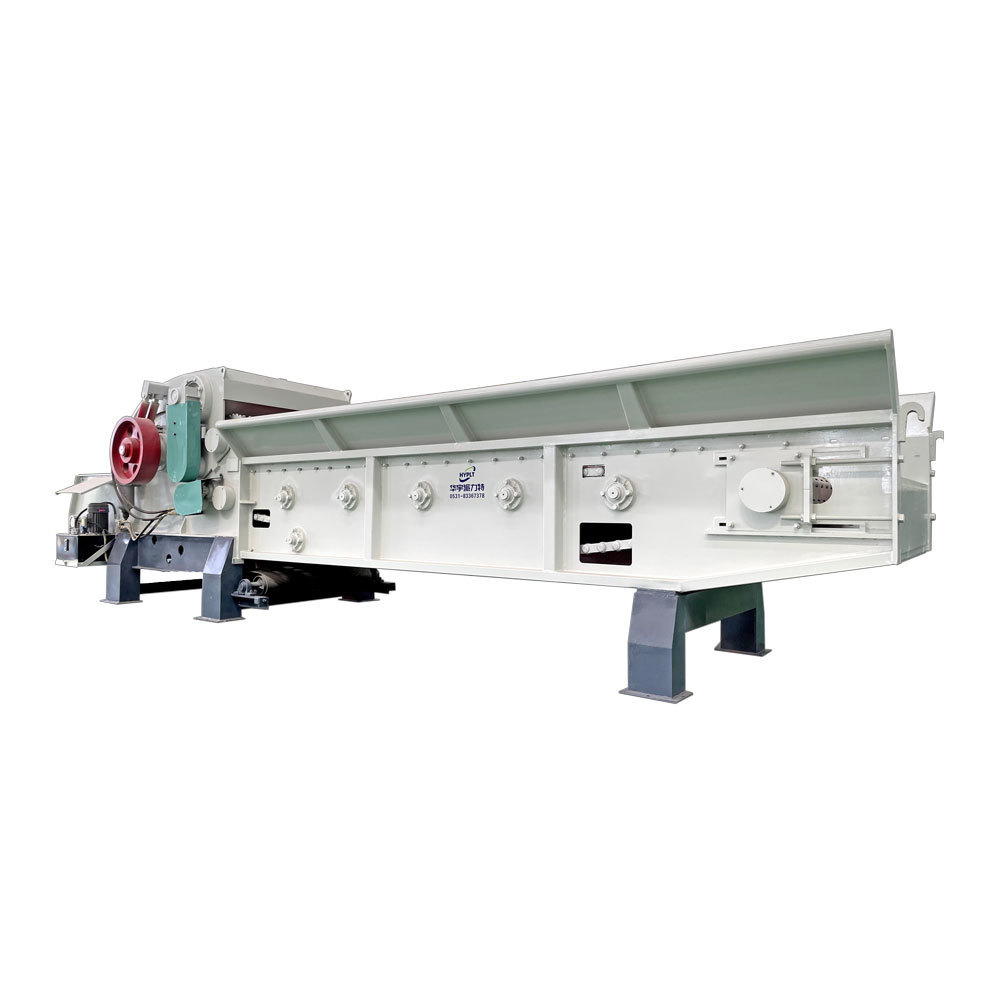
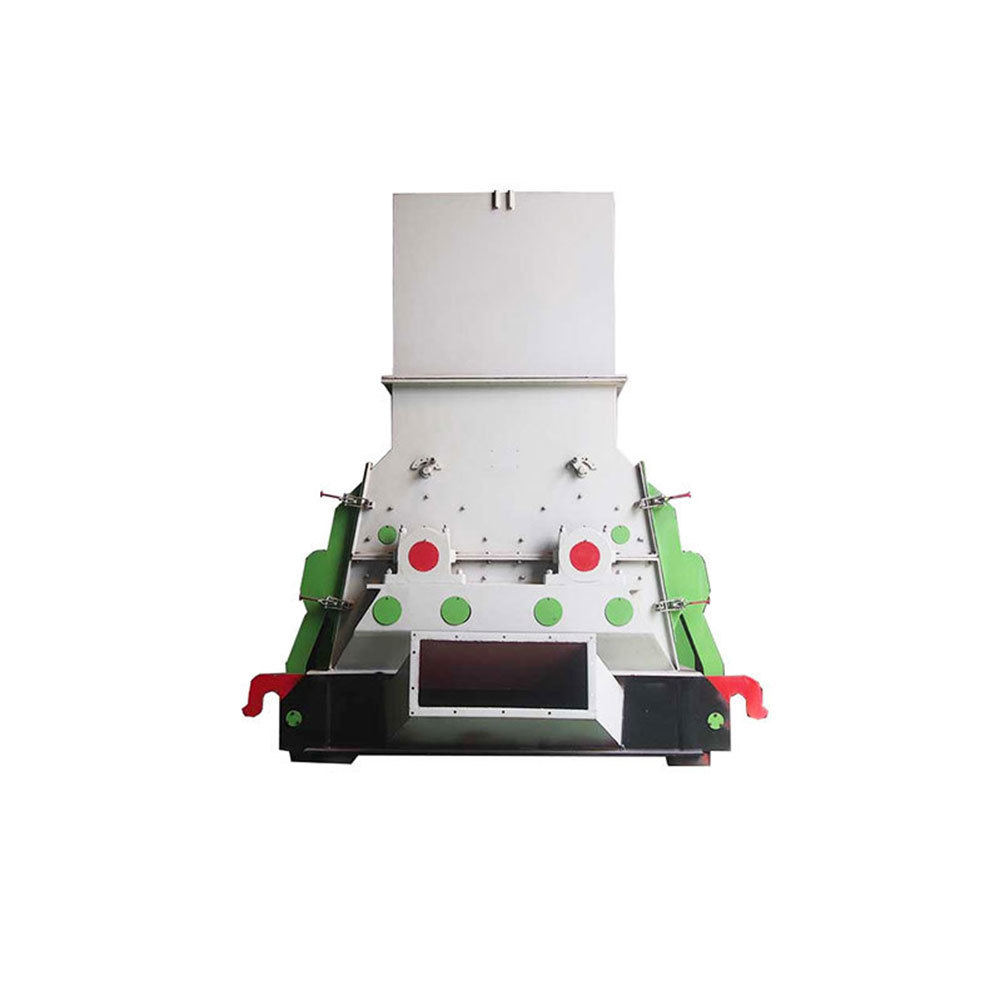
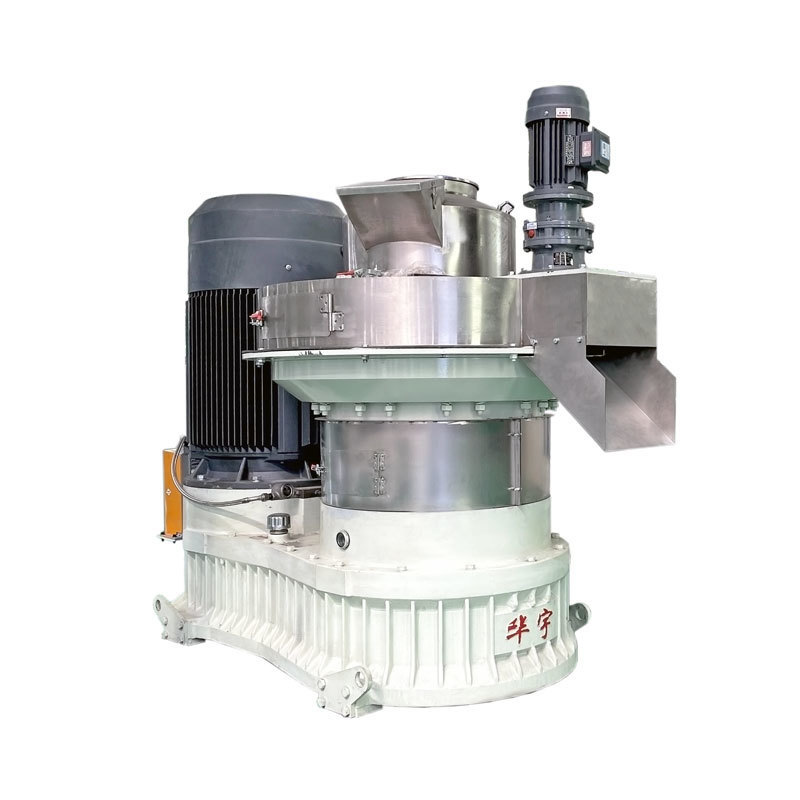
Shredding Machine
Product keywords:
Shredding Machine
Belong to the classification:
Products

Consultation hotline:
Product details
Straw
Straw is a general term for the stem and leaf (ears) portion of mature crops. It usually refers to the remaining parts of wheat, rice, corn, potatoes, rape, cotton, sugarcane and other crops (usually coarse grains) after harvesting the seeds. More than half of the products of photosynthesis of crops exist in straw, which is rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and organic matter, etc. It is a renewable biological resource with multiple uses, and straw is also a kind of coarse feed. It is characterized by high crude fiber content (30%-40%) and contains lignin, etc. Although lignin cellulose cannot be used by pigs and chickens, it can be absorbed and used by ruminant cattle, sheep and other livestock.


Straw in the world
In the United States, there are 24 agricultural states that collect about 45 million tons of straw each year, which is used as feed or to build houses, filling the walls of new houses with whole bales of high-strength extruded straw; in addition, the United States also actively promotes the cause of renewable energy, using straw as an emerging alternative fuel, especially biofuel.
In Europe, a new way to generate electricity from straw has been created.
In Japan, people mainly turn straw into the soil and return it to the fields as fertilizer, but also use it as roughage to feed livestock.
The total theoretical resource of straw in China has reached 1.02 billion tons in 2017, an increase of nearly 400 million tons compared to the early 1990s. Among them, the amount of corn, rice and wheat straw was 430, 240 and 180 million tons, respectively, and the amount of straw of the three major crops accounted for 83.3%. China's straw collectable resources amounted to 840 million tons, and the utilized amount reached 700 million tons, and the comprehensive utilization rate (the ratio of utilized amount to collectable amount) of straw exceeded 83%, of which the utilization rates of straw fertilizer, feed, fuel, base material and raw material were 47.3%, 19.4%, 12.7%, 1.9% and 2.3% respectively, which has formed a fertilizer, feed and other agricultural-oriented The comprehensive utilization pattern of fertilizer and feed has been formed.
Main characteristics of straw
In general, straw consists of 80-90% cells and 10-20% internal cavities, with internal material consisting of 5-10% silica and 5-15% extracts, most of which are water-soluble. In terms of molecules, the straw cell wall is like a woody cell wall, composed of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. Cellulose is gathered in the protofibrils surrounded by molecules. Lignin is the "glue" that connects the individual cells to form the plant tissue and the raw fibers to form the cell wall. Straw differs from wood in its cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin content. Straw has a low cellulose and lignin content, but a high hemicellulose content.
Due to its wood-like composition, straw can be used to make straw pulp or converted into straw pellets. According to the special characteristics of straw, the pelletizing process of straw can be summarized as follows:
1. Raw material preparation stage:
Straw usually has a high dusting potential, which is influenced by the harvesting method. Therefore, the straw needs to be screened from contaminants such as dust and other foreign objects that may affect the quality of the straw pellets, such as stones, metals, and those that may damage the pelletizer in the following procedure.
2. Crushing stage:
The straw biomass is tubular material with a diameter of 4 to 8 mm and a wall thickness of about 0.3 to 0.6 mm. Using a tubular/tube structure, straw can be easily processed and obtained to the desired particle size. Usually, the grinding of straw includes cutting and crushing of straw.
3. Drying stage: Usually, straw is delivered in the form of air-dried bales with a moisture level of about 15%, which is suitable for producing straw pellets. Therefore, the drying process of straw pellets will be omitted. However, if the straw has a large moisture content, the drying step is necessary.
4. Modulation: Straw requires special conditioning to achieve the desired hardness. Straw conditioning involves the application of steam (and/or water) and the addition of binders or additives. Conditioning is required to achieve the necessary temperature and humidity to obtain ductility and to melt the lignin to act as a binder. Binders are needed to enhance the hardness of the pellets and reduce wear during the pelletizing process.
5. Pelletizing: In the pelletizing process, it is necessary to consider the impact of material moisture, density, particle size, fiber strength, natural binders and other factors on pelletizing quality.
Common problems in the pelletizing process of straw pellets are clogging and breakage of the pellet die, overheating, high energy costs or poor quality of pellets, and high maintenance of the pelletizer. In order to avoid the above problems, a high quality pelleting machine is needed.
6. Cooling and sieving: The newly extruded straw pellets are hot and soft, and need to be cooled to obtain the desired hardness, while using the sieve on the cooler to sieve out the pellets with substandard molding.
7. Packaging of finished products: The cooled pellets need to be sent to the finished pellet bin through a professional skirt belt conveyor, and then unloaded from the finished pellet bin and packaged with a packaging scale.
Application scope of straw pellets
Straw pellets are widely used in daily life. Usually, straw pellets are used as animal bedding, animal feed and heating fuel for domestic and industrial use.
Nowadays, straw pellet technology is widely used and straw pellet mills are available worldwide, which makes straw pellets popular for heat and power production.
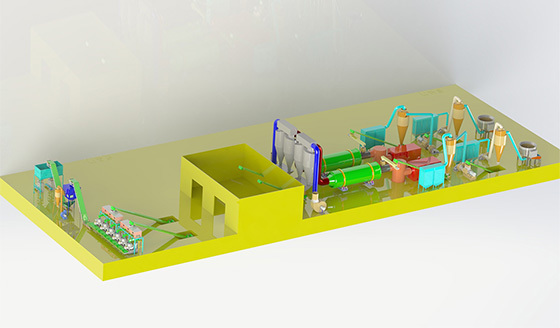
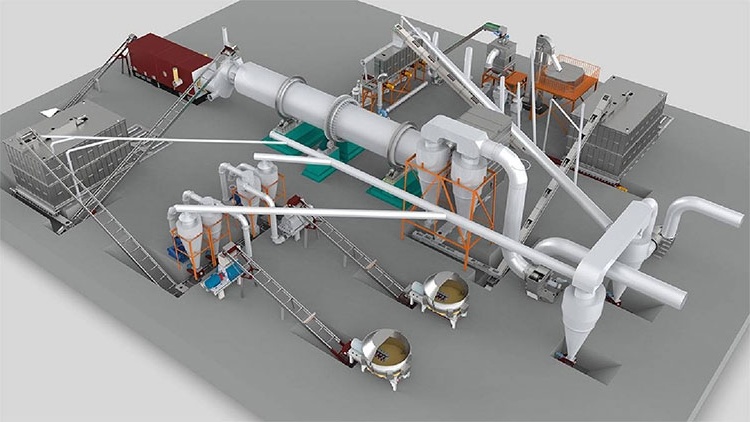
The process of making straw pellets
Straw curing and molding technology is the use of straw, wheat straw, corn straw and other agricultural waste as raw materials, through special equipment straw pellet machine after crushing treatment, compression treatment and other processes, pressed into a solid biomass fuel that can be burned directly.
1. The straw to be pressed will be guillotined or crushed Spin-cutting and crushing machine to control its length below 30mm.
2. The crushed straw will be sent to the drum dryer through the conveyor and the moisture content will be controlled within 10-15%.
3. The raw material after drying is stored in a pile after unloading Shakelong, or stored using a silo. Silo
4. By feeding conveyor, the material is sent into the biomass pellet mill inlet, the machine rotates through the spindle, driving the pressure roller to rotate, and through the rotation of the pressure roller, the material is forced to be extruded into a block from the mold hole, and fall from the outlet.
5. Next, it is sent to the pellet cooler by the special conveyor.
6. After the pellets are cooled, the pellets are sent to the packaging scale or tonnage packaging machine for bagging.
After curing and molding, the biomass pellet fuel has a large specific gravity, small volume, easy to store and transport, is a high-quality solid fuel, its calorific value can reach 3200-4500 calories, with easy to burn, less ash, low cost and other characteristics, can replace firewood, raw coal and other fuels, widely used in heating, living stoves, industrial boilers, biomass power plants, etc.
Straw pellet fuel as a new commodity energy has been used in large quantities in various industries. And because of its high density, high calorific value, regular shape and good fluidity, it is convenient to achieve automatic control of combustion, which can save large amounts of energy costs for enterprises.
Notes on pellet processing:
1. Operating workers should read the instruction manual carefully and be familiar with each process of the equipment before they get on the machine.
2. The production process should be operated in strict accordance with the regulations and sequential order, and the installation operation should be carried out according to its requirements.
3. The host equipment needs to be installed and fixed on the horizontal cement ground, reinforced tight screws.
4. Smoking and open fire are strictly prohibited in the production site.
5. Each time after the machine is turned on, it needs to idle for a few minutes first, idle to confirm that the pressure wheel fits the mold rotation before feeding.
6. It is strictly forbidden to add stones, metals and other hard debris to the feeding device, and do a good job of removing iron before granulation to avoid damage to the granulation chamber.
7. During the operation of the equipment, it is strictly forbidden to use hands or other tools to dial the material to avoid danger.
8. If there is any abnormal noise during the production process, you need to immediately cut off the power supply, check and deal with abnormalities before turning on the machine to continue production.
9. Before stopping the machine, stop the auxiliary feed first, then put the oil, wait until the die hole is full of oil, no oil in the granulating chamber before stopping. The purpose of putting oil material is to make it easier to discharge material when producing next time.
According to the requirements of the correct operation of the pellet mill, and in accordance with the requirements of attention to matters related to not only improve the output and running performance of the equipment, but also to extend the service life of the equipment.
Previous page
next page
Previous page
Integrated Crusher
next page
Related products
Online message consultation